What is Generative Design?
Generative Design is a toolset and process for design exploration. You can enter your design objectives into Generative Design, alongside parameters such as performance requirements, materials, manufacturing methods and the cost constraints. The toolset then quickly generates, utilizing the cloud and numerous design alternatives, allowing you to explore all working outcomes.

What are the benefits for Manufacturers?
All companies have and will continue to design, engineer, and manufacture their products in their own way. However, Generative Design is here to help provide insights into alternative and optimized outcomes. It is easier to break down the various benefits, as different businesses will look for different outcomes.
Fast-track product development:
The Generative Design process factors in manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing, 5-axis, 3-axis and more methods, at an early design stage in the development process. Meaning that generated outcomes already factor in what manufacturing facilities you and your business have access to, allowing you to get to market faster.
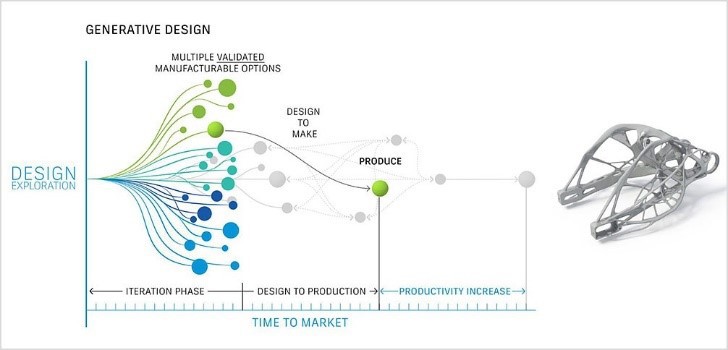
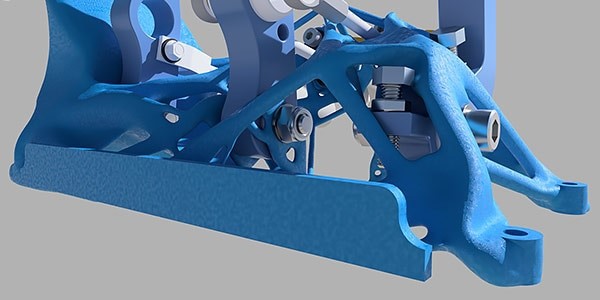
Light weighting:
Examples you will see from Generative Design have an obvious lack of material when compared with more traditional outcomes. This is an integral part of the calculations happening within the algorithm. Enhancing mass and material use, while maintaining high-performance standards and engineering constraints.

Improved performance:
Generative Design helps to improve and elevate your product's durability, whilst eliminating areas of weakness from a design. Offering you and your business different possibilities, that may not have come to the surface otherwise.

Part consolidation:
With the increasing use and accessibility of additive manufacturing techniques, combined with Generative Design outcomes. Offers the possibility to consolidate multiple components into fewer solid parts.
Sustainability:
The Generative Design process can help you meet your sustainability goals, through light-weighting, minimizing waste, and highlighting more sustainable materials.

What are others doing with this technology already?
Generative Design has been in development for some time, is not new to Autodesk. This means there are a lot of businesses that have already benefited from this technology and the benefits highlighted above. To round out this first article and to offer some inspiration as to where you and your business could use this unique technology. We wanted to illustrate a few examples to show the breadth of outcomes that can be achieved alongside the gains experienced by the businesses involved.
- Claudius Peters - Engineers at this machine and process plant provider used generative design to reinvent elements of their clinker cooler product, helping to reduce materials by 25%. Learn more.
- General Motors - GM and Autodesk engineers apply Generative Design technology to reconceive a small, but important, vehicle component. The resulting part is 40% lighter and 20% stronger than the original part. Learn more.
- Edera Safety - Using Generative Design, adamsfour, an in-house Edera Safety brand focused on reducing spinal cord injuries, has created a new back-protection system for athletes. Learn more.
- Volkswagen Group of America - Exploring Generative Design to reduce wheel weight and find a modern aesthetic, Volkswagen Group of America also realizes significant reduction in development time. Learn more.
I hope you found this helpful! Look out for our next Generative Design Manufacturing-focused article, where I will explore the technologies and workflows available to you and your businesses, making the above possible today.









